Pages
Health Care News
Categories
- Asthma education
- Autism
- Canadian Health&Care Mall
- Cardiac function
- Critical Care Units
- Follicle
- Health
- health care medical transport
- health care programs
- Health&Care Professionals
- Hemoptysis
- Hormone
- Isoforms
- Nitroglycerin Patches
- Profile of interleukin-10
- Progesterone
- Pulmonary Function
- Sertoli Cells
- Theophylline
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula
Canadian HealthCare News
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: MATERIALS AND METHODS(5)
 Afterthree washes in TBS with 0.1% Tween 20 and 15-min block in TBS with milk, membranes were incubated with a donkey anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) for 1 h at room temperature. After five further washes, antibody binding was detected with the Western Lightning Chemiluminescence reagent (Perkin Elmer Life Sciences, Boston, MA) and Kodak X-Omat blue XB-1 films.
(more…)
Afterthree washes in TBS with 0.1% Tween 20 and 15-min block in TBS with milk, membranes were incubated with a donkey anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) for 1 h at room temperature. After five further washes, antibody binding was detected with the Western Lightning Chemiluminescence reagent (Perkin Elmer Life Sciences, Boston, MA) and Kodak X-Omat blue XB-1 films.
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: MATERIALS AND METHODS(4)
Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
Epididymis was harvested from anesthetized rats. Tissue was cut into small pieces and rinsed several times in PBS/protease inhibitors to remove most of the sperm. Tissue was homogenized in 10 ml/g of buffer containing 250 mM sucrose, 18 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, and complete protease inhibitor (Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN), adjusted to pH 7.4 with HEPES, using a PRO 200 homogenizer followed by 20 strokes in a glass potter fitted with a Teflon pestle (Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ).
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: MATERIALS AND METHODS(3)
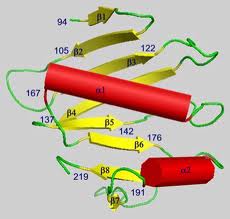 Sections were washed in PBS (3X for 5 min) and then blocked in PBS containing 1% BSA for 15 min. Primary antibodies were applied in a moist chamber for 90 min at room temperature or overnight at 4°C. Sections were washed in high-salt PBS (2.7% NaCl) twice for 5 min and once in normal PBS. Secondary antibody was then applied for 1 h at room temperature followed by washes as described above. Slides were mounted in Vectashield medium (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA). Some sections were double-stained by subsequent incubation with another primary antibody raised in a different species, followed by an appropriate secondary antibody.
(more…)
Sections were washed in PBS (3X for 5 min) and then blocked in PBS containing 1% BSA for 15 min. Primary antibodies were applied in a moist chamber for 90 min at room temperature or overnight at 4°C. Sections were washed in high-salt PBS (2.7% NaCl) twice for 5 min and once in normal PBS. Secondary antibody was then applied for 1 h at room temperature followed by washes as described above. Slides were mounted in Vectashield medium (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA). Some sections were double-stained by subsequent incubation with another primary antibody raised in a different species, followed by an appropriate secondary antibody.
(more…)
6Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: MATERIALS AND METHODS(2)
Immunofluorescence: Conventional and Confocal Microscopy
Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, MA) were acquired, retained, and used in compliance with the National Research Council’s recommendations. Sexually mature male rats were anesthetized with Nembutal (0.5 ml i.p.; Abbott Laboratories, North Chicago, IL) and perfused via the left ventricle with PBS (0.9% NaCl in 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) followed by fixative containing 4% paraformaldehyde, 10 mM sodium periodate, 75 mM lysine, and 5% sucrose in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (PLP), as described previously.
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: MATERIALS AND METHODS(1)
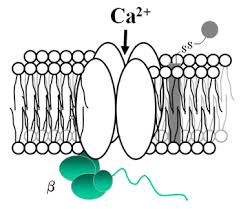 Antibodies
Affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibodies against the V-ATPase C1,C2, G1, G3, a1, a2, a4, d1, and d2 subunit isoforms were used. These antibodies have been characterized previously. An affinity-purified polyclonal antibody raised in chicken against the V-ATPase E2 subunit was also used to identify narrow and clear cells. A novel affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibody against the last 10 amino acids (CMQNAFRSLE) of the C-terminal tail of the V-ATPase A subunit was also used and was characterized in this study.
(more…)
Antibodies
Affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibodies against the V-ATPase C1,C2, G1, G3, a1, a2, a4, d1, and d2 subunit isoforms were used. These antibodies have been characterized previously. An affinity-purified polyclonal antibody raised in chicken against the V-ATPase E2 subunit was also used to identify narrow and clear cells. A novel affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibody against the last 10 amino acids (CMQNAFRSLE) of the C-terminal tail of the V-ATPase A subunit was also used and was characterized in this study.
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: INTRODUCTION(4)
Four a subunit isoforms have been identified in the human V-ATPase: al, a2, a3, and a4. Subunit al is expressed ubiquitously; subunit a2 was detected in the kidney, lung, and spleen; and subunit a3 was localized in osteoclasts, where it is essential for bone resorption. Subunit a4 was detected in the kidney, inner ear, and the murine epididymis. Two d subunit isoforms have been identified for the human V-ATPase: dl is ubiquitous, whereas d2 is present in kidney, lung, and osteoclast.
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: INTRODUCTION(3)
 In addition, some of these subunits have more than one isoform encoded by different genes and with different tissue and subcellular expression patterns. Only one form has been identified for the A subunit of the human V-ATPase. This ubiquitous subunit has a nucleotide-binding site and is thought to be the catalytic subunit of the V-ATPase. Subunit B is present in two isoforms: the B1 isoform, originally called the kidney isoform of the 56-kDa subunit, and the B2 isoform, originally called the brain isoform of the 56-kDa subunit. Subunits C, G, and E are part of the peripheral stalk that connects the V1 and V0 domains of the V-ATPase.
(more…)
In addition, some of these subunits have more than one isoform encoded by different genes and with different tissue and subcellular expression patterns. Only one form has been identified for the A subunit of the human V-ATPase. This ubiquitous subunit has a nucleotide-binding site and is thought to be the catalytic subunit of the V-ATPase. Subunit B is present in two isoforms: the B1 isoform, originally called the kidney isoform of the 56-kDa subunit, and the B2 isoform, originally called the brain isoform of the 56-kDa subunit. Subunits C, G, and E are part of the peripheral stalk that connects the V1 and V0 domains of the V-ATPase.
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: INTRODUCTION(2)
Thus, in each individual cell type, the V-ATPase functions in a variety of distinct cellular processes.
The V-ATPase is a complex enzyme that is composed of many subunits and is divided into two distinct sectors. The V0 sector is responsible for proton translocation and is composed of the transmembrane subunits previously designated by the lowercase letters a, c, c', c'', and d. The V1 sector forms a large cytosolic domain composed of eight subunits, designated by the uppercase letters A-H in a stoichiometry of A3B3CDEFG2H and is anchored to the plasma membrane via its interaction with the V0 domain.
(more…)
Distinct Expression Patterns of Different Subunit Isoforms: INTRODUCTION(1)
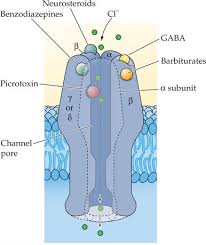 The vacuolar-H+ATPase (V-ATPase) is a multisubunit enzyme that couples ATP hydrolysis to proton pumping across membranes. It is ubiquitously expressed in eukaryotic cells, where it participates in the acidification of highly differentiated organelles, including the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, endo-somes, and secretory vesicles. In addition, the V-ATPase is also found at high density in the plasma membrane of specialized epithelial cells that are involved in active proton transport and pH regulation of extracellular compartments, such as narrow and clear cells in the epididymis and vas deferens, renal intercalated cells, osteoclasts, or some cell types in the inner ear, including interdental cells, which resemble renal intercalated cells.
(more…)
The vacuolar-H+ATPase (V-ATPase) is a multisubunit enzyme that couples ATP hydrolysis to proton pumping across membranes. It is ubiquitously expressed in eukaryotic cells, where it participates in the acidification of highly differentiated organelles, including the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, endo-somes, and secretory vesicles. In addition, the V-ATPase is also found at high density in the plasma membrane of specialized epithelial cells that are involved in active proton transport and pH regulation of extracellular compartments, such as narrow and clear cells in the epididymis and vas deferens, renal intercalated cells, osteoclasts, or some cell types in the inner ear, including interdental cells, which resemble renal intercalated cells.
(more…)
Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: DISCUSSION(10)
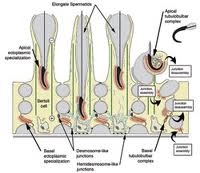 One of the major proteins regulated by FSH and secreted by Sertoli cells into the lumen is ABP. In the present study, LM immunocytochemistry revealed that ABP was expressed intensely in Sertoli cells, but the reaction was dramatically reduced in FORKO mice, a finding confirmed by the Western blot analyses. This may be due to the dilated nature of the Sertoli cell cytoplasm and its effect on secretory organelles, such as the Er and Golgi apparatus, which appeared to be less prominent than in wild-type mice and which would affect secretion. However, it is equally possible that regulation is affected at the mRNA level.
(more…)
One of the major proteins regulated by FSH and secreted by Sertoli cells into the lumen is ABP. In the present study, LM immunocytochemistry revealed that ABP was expressed intensely in Sertoli cells, but the reaction was dramatically reduced in FORKO mice, a finding confirmed by the Western blot analyses. This may be due to the dilated nature of the Sertoli cell cytoplasm and its effect on secretory organelles, such as the Er and Golgi apparatus, which appeared to be less prominent than in wild-type mice and which would affect secretion. However, it is equally possible that regulation is affected at the mRNA level.
(more…)
