Pages
Health Care News
Categories
- Asthma education
- Autism
- Canadian Health&Care Mall
- Cardiac function
- Critical Care Units
- Follicle
- Health
- health care medical transport
- health care programs
- Health&Care Professionals
- Hemoptysis
- Hormone
- Isoforms
- Nitroglycerin Patches
- Profile of interleukin-10
- Progesterone
- Pulmonary Function
- Sertoli Cells
- Theophylline
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula
Category Archives: Hormone
Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: MATERIALS AND METHODS(2)
 The remaining right testis of each animal was kept intact and immediately fixed by cardiac perfusion with 2.5% or 5% glutaraldehyde buffered in sodium cacodylate (0.1 M) containing 0.05% calcium chloride (pH 7.4). After 10 min of perfusion, the right testes were removed from the scrotum, cut into small 1-mm cubes and placed in the same fixative for an additional 2 h at 4°C. Thereafter, the tissues were thoroughly rinsed three times in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer containing 0.2 M sucrose and left in this buffer overnight.
(more…)
The remaining right testis of each animal was kept intact and immediately fixed by cardiac perfusion with 2.5% or 5% glutaraldehyde buffered in sodium cacodylate (0.1 M) containing 0.05% calcium chloride (pH 7.4). After 10 min of perfusion, the right testes were removed from the scrotum, cut into small 1-mm cubes and placed in the same fixative for an additional 2 h at 4°C. Thereafter, the tissues were thoroughly rinsed three times in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer containing 0.2 M sucrose and left in this buffer overnight.
(more…) Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: MATERIALS AND METHODS(1)
Animals
This investigation was approved by the ethics committee of the Clinical Institute of Montreal and McGill University and was conducted according to accepted standards of animal experimentation. The FORKO mice were generated by homologous recombination as described by Dierich et al.. This alteration eliminates the entire repertoire of FSH-R forms, producing complete loss of hormone signaling. Breeding F2 heterozygous males and females produced mice of all three genotypes in the SV129 background.
(more…)
Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: INTRODUCTION(3)
 While Sertoli cells respond to FSH stimulation, the nature of the response itself varies depending on the developmental status of the animal. Early studies demonstrated that FSH acts as a Sertoli cell mitogen in the prenatal and newborn animal and is instrumental in determining the final spermatogenic capability of the testis. In immature mice, it has been shown that FSH-R signaling appears to be essential for testicular development, the initiation of the first wave of spermatogenesis, and sexual maturity.
(more…)
While Sertoli cells respond to FSH stimulation, the nature of the response itself varies depending on the developmental status of the animal. Early studies demonstrated that FSH acts as a Sertoli cell mitogen in the prenatal and newborn animal and is instrumental in determining the final spermatogenic capability of the testis. In immature mice, it has been shown that FSH-R signaling appears to be essential for testicular development, the initiation of the first wave of spermatogenesis, and sexual maturity.
(more…) Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: INTRODUCTION(2)
Also important is the fact that Sertoli cells transport water from the interstitial space into the lumen, serving as the vehicle for moving sperm from the testis to the epididymis. In addition to basolaterally locatedion channels, recent studies have revealed that aquaporins (water channels) are abundant in the testis, with some being localized to Sertoli cells. Interestingly, various members of the aquaporin gene family contain CRE motifs (CREB binding regions) and are under cAMP regulation, a second messenger that is activated upon FSH-R signaling.
(more…)
Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: INTRODUCTION(1)
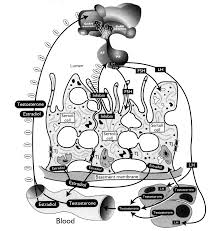 Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), a heterodimeric pituitary glycoprotein hormone considered essential for mammalian fertility, interacts specifically with its cognate receptor (FSH-R) localized in Sertoli and ovarian granulosa cells. The FSH-R, derived from a single gene, is produced as a Gs-protein coupled, seven-transmembrane receptor, which activates several signaling pathways to integrate target cellular activities.
(more…)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), a heterodimeric pituitary glycoprotein hormone considered essential for mammalian fertility, interacts specifically with its cognate receptor (FSH-R) localized in Sertoli and ovarian granulosa cells. The FSH-R, derived from a single gene, is produced as a Gs-protein coupled, seven-transmembrane receptor, which activates several signaling pathways to integrate target cellular activities.
(more…) 