Pages
Health Care News
Categories
- Asthma education
- Autism
- Canadian Health&Care Mall
- Cardiac function
- Critical Care Units
- Follicle
- Health
- health care medical transport
- health care programs
- Health&Care Professionals
- Hemoptysis
- Hormone
- Isoforms
- Nitroglycerin Patches
- Profile of interleukin-10
- Progesterone
- Pulmonary Function
- Sertoli Cells
- Theophylline
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula
 |
Canadian Health&Care; MallVisit the most reliable Canadian Health&Care; Mall offering a wide choice of drugs for any medical emergency you may have, from male health to infections and obesity! Making sure you always spend less money is among our top priorities! |
Structural and Functional Modifications of Sertoli Cells: INTRODUCTION(1)
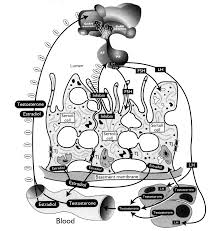 Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), a heterodimeric pituitary glycoprotein hormone considered essential for mammalian fertility, interacts specifically with its cognate receptor (FSH-R) localized in Sertoli and ovarian granulosa cells. The FSH-R, derived from a single gene, is produced as a Gs-protein coupled, seven-transmembrane receptor, which activates several signaling pathways to integrate target cellular activities.
In the testis, FSH has a differential effect on Sertoli cells in accordance with the different stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. While the hormone is maximally bound at stage I, FSH stimulated cAMP production peaks at stage IV, with cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) mRNA levels peaking at stage VII of the cycle. In the adult testis, the nondividing population of Sertoli cells performs diverse functions. In addition to anchoring and nourishing germ cells, they form the blood testis barrier, phagocytose residual bodies, release sperm at the time of spermiation, and participate in secretion and endocytosis of various substances, including ions and proteins.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), a heterodimeric pituitary glycoprotein hormone considered essential for mammalian fertility, interacts specifically with its cognate receptor (FSH-R) localized in Sertoli and ovarian granulosa cells. The FSH-R, derived from a single gene, is produced as a Gs-protein coupled, seven-transmembrane receptor, which activates several signaling pathways to integrate target cellular activities.
In the testis, FSH has a differential effect on Sertoli cells in accordance with the different stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. While the hormone is maximally bound at stage I, FSH stimulated cAMP production peaks at stage IV, with cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) mRNA levels peaking at stage VII of the cycle. In the adult testis, the nondividing population of Sertoli cells performs diverse functions. In addition to anchoring and nourishing germ cells, they form the blood testis barrier, phagocytose residual bodies, release sperm at the time of spermiation, and participate in secretion and endocytosis of various substances, including ions and proteins.
Tags: follicle-stimulating hormone receptor male reproductive tract Sertoli cells sperm testis
